✔ 100% Authentic Product
👁️ Currently Viewing 2096
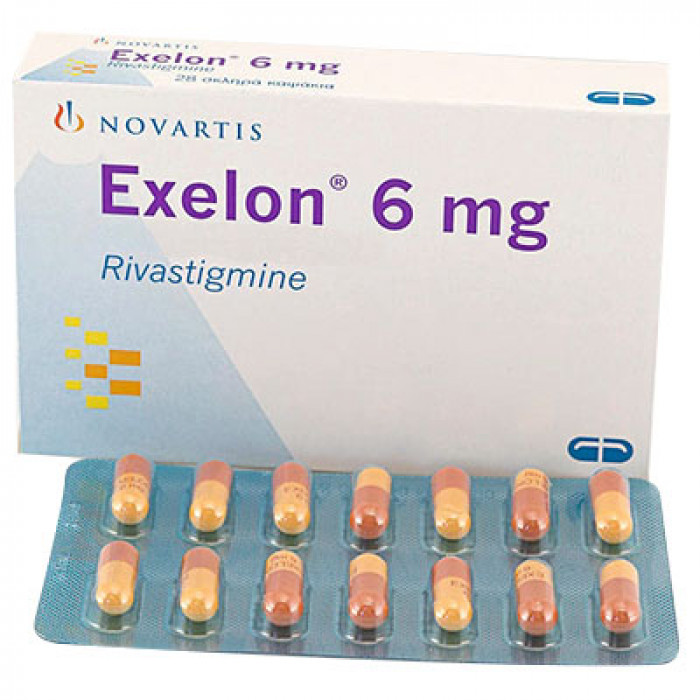
Type: Caps. Generic Name:Rivast1gmine (as hydrogen tartrate) 1 .5mg. 3mg. 4.5mg & 6mg/capsule Manufacturer/Distributor: Novartis
Discount
Price: ৳ 2,850
MRP:
৳
3000
5%
Off
✅ Description:
Indications
Treatment for mild to moderately severe Alzheimer's disease symptoms. In individuals with idiopathic Parkinson's disease, symptomatic therapy of mild to moderately severe dementia is used.
Pharmacology
Rivastigmine is a carbamate derivative similar to physostigmine but not donepezil or tacrine in structure. The exact mechanism of rivastigmine is unknown, however it is thought that rivastigmine binds reversibly to and inactivates chlolinesterase (e.g., acetylcholinesterase, butyrylcholinesterase), inhibiting acetycholine hydrolysis and therefore increasing acetylcholine content at cholinergic synapses. When compared to acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase in peripheral tissues, rivastigmine's anticholinesterase action is relatively selective for brain acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase.
Dosage & Administration
Rivastigmine capsule-
Initial dose: Rivastigmine 1.5 mg twice a day.
Dose titration: The starting dose is Rivastigmine 1.5 mg twice a day. If this dose is well tolerated after a minimum of two weeks of treatment, the dose may be increased to Rivastigmine 3 mg twice a day. Subsequent increases to 4.5 mg and then 6 mg twice a day should also be based on good tolerability of the current dose and may be considered after a minimum of two weeks of treatment at that dose level.
Maintenance dose: The effective dose is 3 mg to 6 mg twice a day; to achieve maximum therapeutic benefit patients should be maintained on their highest well tolerated dose. The recommended maximum daily dose is 6 mg twice a day. Maintenance treatment can be continued for as long as a therapeutic benefit for the patient exists.
Re-initiation of therapy: If treatment is interrupted for more than several days, it should be re-initiated at 1.5 mg twice daily. Dose titration should then be carried out as described above.
Rivastigmine transdermal patch: Apply patch on intact skin for a 24-hour period; replace with a new patch every 24 hours.
Initial Dose: Initiate treatment with 4.6 mg/24 hours Rivastigmine transdermal patch.
Dose Titration: After a minimum of 4 weeks, if tolerated, increase dose to 9.5 mg/24 hours, which is the minimum effective dose. Following a minimum additional 4 weeks, may increase dosage to maximum dosage of 13.3 mg/24 hours.
Mild to Moderate Alzheimer's Disease and Parkinson’s Disease Dementia: Rivastigmine transdermal patch 9.5 mg/24 hours or 13.3 mg/24 hours once daily.
Severe Alzheimer’s Disease: Rivastigmine transdermal patch 13.3 mg/24 hours once daily.
For treatment interruption longer than 3 days, retitrate dosage starting at 4.6 mg per 24 hours.
Rivastigmine should be administered twice a day, with morning and evening meals.
Interaction
As a cholinesterase inhibitor, rivastigmine may exaggerate the effects of succinylcholine-type muscle relaxants during anesthesia. Care should be taken when choosing anesthetics. If necessary, consider possible dose adjustments or temporarily stop treatment. In view of its pharmacodynamic effects, rivastigmine should not be administered simultaneously with other cholinergic substances, and may interfere with the activity of anticholinergic drugs. No pharmacokinetic interaction between rivastigmine and digoxin, warfarin, diazepam or fluoxetine was observed in the study of healthy volunteers. Warfarin-induced increase in prothrombin time was not affected by the administration of rivastigmine. After digoxin and rivastigmine were used in combination, no adverse effects on cardiac conduction were observed.
Contraindications
The use of this medicinal product is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to the active substance or other carbamate derivatives.
Side Effects
The most common adverse effects are gastrointestinal, with nausea (38%) and vomiting (23%) being the most prevalent, especially during titration. In clinical tests, female patients were found to be more sensitive to gastrointestinal side effects and weight loss than male ones.
Pregnancy & Lactation
There are no clinical data on Rivastigmine. Rivastigmine should only be taken if absolutely required during pregnancy. Rivastigmine is secreted in milk by animals. There is no information on whether rivastigmine is excreted in human milk. As a result, women who are on rivastigmine should not breastfeed.
Precautions & Warnings
Patients with sick sinus syndrome or conduction abnormalities, as well as patients with respiratory disorders. Gastric acid production may be increased by cholinergic activation. Urinary obstruction and convulsions may be worsened. Pregnancy. Renal failure, as well as mild to moderate hepatic failure. Keep an eye on your weight if you have asthma or obstructive pulmonary disease. Extrapyramidal symptoms may become worse. Lactation.
Storage Conditions
Store in a cool and dry place, protected from light.
⚠️Disclaimer:
At ePharma, we’re committed to providing accurate and accessible health information. However, all content is intended for informational purposes only and should not replace medical advice from a qualified physician. Please consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance. We aim to support, not substitute, the doctor-patient relationship.