✔ 100% Authentic Product
👁️ Currently Viewing 1893
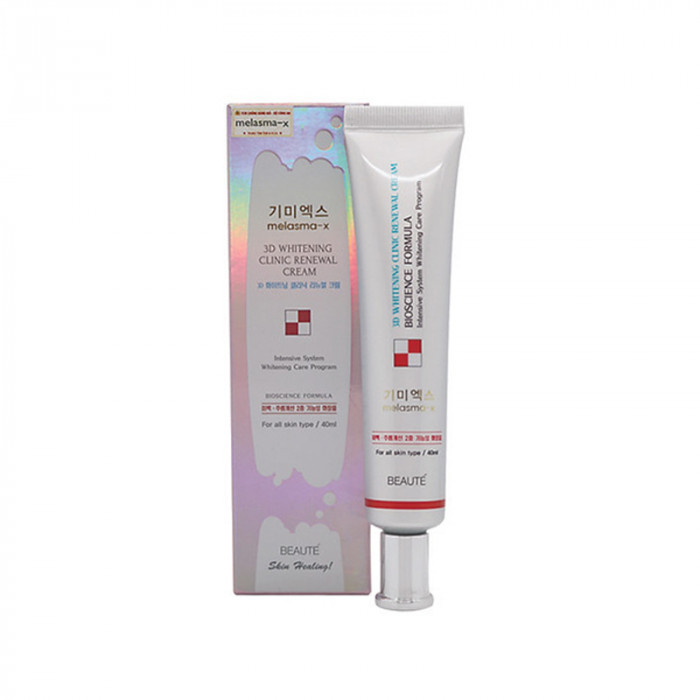
Beaute Melasma X 3D Whitening Clinic Mask Pack 30ml
The Beaute Melasma-X 3D Whitening Clinic Mask Pack is a premium skincare solution designed to address hyperpigmentation, melasma, and uneven skin tone while promoting a radiant and youthful complexion.
Discount
Price: ৳ 270
MRP:
৳
275
2%
Off

100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed

Safe & Secure Payments, Always

Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery

Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed
Safe & Secure Payments, Always
Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery
Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
✅ Description:
3D Contouring Fabric:
- The mask is made from a 3D fabric that contours to the shape of your face, providing optimal coverage and maximizing the absorption of the active ingredients for better results.
Whitening & Brightening Formula:
- This specially formulated mask is designed to lighten dark spots, even out skin tone, and improve the appearance of melasma and hyperpigmentation, resulting in a brighter and more uniform complexion.
Hydrating & Nourishing:
- Infused with deeply moisturizing ingredients, this mask helps keep the skin soft, smooth, and hydrated, ensuring long-lasting moisture.
Anti-Aging Properties:
- The mask works to reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, helping the skin look youthful, plump, and rejuvenated.
Clinically Tested:
- Dermatologically approved, this mask is designed to be safe for all skin types, including sensitive skin, providing peace of mind when using it regularly.
✔️ Benefits:
Targeted Treatment for Melasma:
- The mask is specifically designed to target melasma and other pigmentation issues, working to reduce the appearance of dark spots and promote an even skin tone.
Radiant Skin:
- With its brightening formula, the mask helps lighten dark spots and dullness, boosting your skin's natural radiance for a glowing complexion.
Enhanced Hydration:
- Deeply moisturizing ingredients keep your skin fresh, plump, and nourished, ensuring it stays hydrated throughout the day.
Smooth and Youthful Appearance:
- By reducing fine lines and wrinkles, the mask helps to smooth out your skin’s texture, leaving it looking youthful and rejuvenated.
At-Home Salon Experience:
- The mask delivers professional-level results, allowing you to experience a salon-quality whitening treatment in the comfort of your own home.
✔️ How to Use:
- Cleanse: Start by thoroughly cleansing your face to remove any dirt, oil, or makeup.
- Apply the Mask: Unfold the mask and apply it to your face, ensuring it fits comfortably over your eyes, nose, and mouth for full coverage.
- Leave On: Allow the mask to sit for 15-20 minutes, giving the ingredients time to penetrate your skin.
- Remove the Mask: Gently remove the mask and lightly pat the remaining serum into your skin for full absorption.
- Follow with Your Skincare Routine: Finish by applying your usual moisturizer or sunscreen to seal in the benefits.
⚠️Disclaimer:
At ePharma, we’re committed to providing accurate and accessible health information. However, all content is intended for informational purposes only and should not replace medical advice from a qualified physician. Please consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance. We aim to support, not substitute, the doctor-patient relationship.