✔ 100% Authentic Product
👁️ Currently Viewing 2390
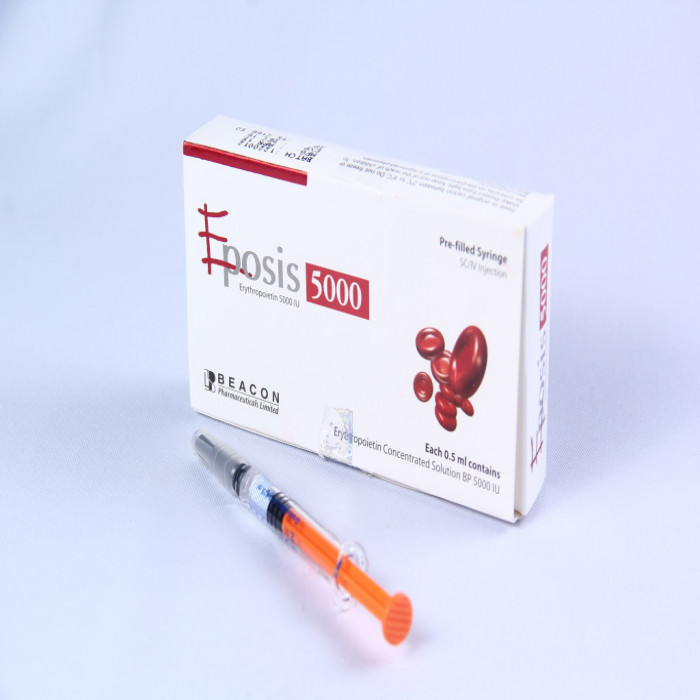
Generic Name: Erythropoietin 5000IU
Manufacturer/Distributor: Beacon Pharmaceuticals Ltd.
Discount
Price: ৳ 2,059
MRP:
৳
2167
5%
Off

100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed

Safe & Secure Payments, Always

Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery

Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed
Safe & Secure Payments, Always
Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery
Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
✅ Description:
Indications of Eposis 5000 IU
Erythropoietin is used to treat anemia associated with chronic renal failure in both dialysis and non-dialysis patients.
Anemia in patients with non-myeloid malignancies who are experiencing anemia as a result of concurrent treatment.
To decrease the need for allogeneic blood transfusions, anemic patients (hemoglobin >10 to 13 g/dL) are scheduled for elective, noncardiac, and nonvascular surgery. In HIV-positive patients, anemia is linked to zidovudine medication.
Dosage and Administration of Eposis 5000 IU
Treatment of anemia in chronic renal failure: Erythropoietin is administered to maintain hemoglobin concentration between 11 to 12 g/dl and hematocrit of 33-36 % in adults.
Starting dose:
Adult: Usually 50 to 100 lU/kg three times in a week (TIW) by IV or Subcutaneous route.
Pediatric: 50 lU/kg TIW by IV or Subcutaneous route.
Dose adjustment: The dose should be increased if hematocrit does not increase by 5 to 6 points after 8 weeks of therapy, and hematocrit is below the suggested target range. The dose should be reduced when hematocrit approaches 36% or hematocrit increases >4 points in any 2-week period.
Maintenance dose: Maintenance dose must be individualized for each patient. In patients undergoing dialysis, the median maintenance dose is 75 lU/kg TIW, with a range from 12.5 to 525 lU/kg TIW as directed by the physician. In CRF patients not on dialysis, the maintenance dose is 75 to 150 lU/kg/week.
Treatment of Anemia in Cancer Patients on Chemotherapy:
Starting dose:
Adult: 150 lU/kg TIW by Subcutaneous route or 40,000 IU Subcutaneous route weekly.
Pediatric: 25 to 300 lb/kg 3 to 7 times per week by Subcutaneous or IV route.
Dose adjustment: If the response is not satisfactory, the dose should be increased to 300 lU/kg TIW. If the hematocrit exceeds 40%, the dose should be withheld until the hematocrit falls to 36%. The dose should be reduced to 25% when treatment is resumed and titrated to maintain the desired hematocrit.
Surgery Patients: The recommended dose is 300 lU/kg/day subcutaneously for 10 days before surgery, on the day of surgery, and for 4 days after surgery. An alternate dose schedule is 600 lU/kg subcutaneously in a once-weekly doses (21, 14, and 7 days before surgery) plus a fourth dose on the day of surgery.
Zidovudine-treated HIV-infected Patients:
Starting dose
Adult: 100 lU/kg as an IV or Subcutaneous injection TIW for 8 weeks.
Pediatric: 50 to 400 lU/kg 2 to 3 times per week by Subcutaneous or IV route.
Dose adjustment: If the response is not satisfactory, the dose should be increased by 50-1001U/kg TIW. Response should be evaluated every 4 to 8 weeks thereafter and the dose adjusted accordingly by 50 to 100 lU/kg increments TIW.
Maintenance dose: The dose is titrated to maintain the hematocrit between 33-36%.
Contraindications
In patients with uncontrolled hypertension, erythropoietin is contraindicated.
Hypersensitivity to mammalian cell-derived products is well-known.
Hypersensitivity to Erythropoietin or any of the preparation's components.
Side Effects of Eposis 5000 IU
Headache, dizziness, fever, malaise, arthralgia, and hyperkalemia are common symptoms. Cardiovascular: The most prevalent side effect is hypertension, followed by palpitations. Nausea, vomiting, anorexia, and diarrhea are common gastrointestinal symptoms. Allergic responses are common.
Pregnancy & Lactation
Pregnancy Classification C. Because there are no controlled trials of erythropoietin in pregnant women and animal reproduction studies are not necessarily predictive of human responses, erythropoietin should only be taken if plainly needed during pregnancy. This medication is not known to be excreted in human milk. Because many medicines are excreted in human milk, erythropoietin should be given with caution to a nursing mother.
Precautions & Warnings
In individuals with controlled hypertension, ischemic vascular disease, a history of seizures, or a suspected allergy to the substance, erythropoietin should be administered with caution.
Iron evaluation: The patient's iron storage, particularly transferrin saturation, and serum ferritin, should be assessed before and during Erythropoietin therapy. The saturation of transferrin should be at least 20%, and the ferritin level should be at least 100 ng/ml. To increase or maintain transferrin saturation levels that will sufficiently support erythropoiesis, almost all patients will require supplementary Iron.
Storage Conditions
Erythropoietin should be stored between 2 and 8 degrees Celsius. Protect yourself from the sun. Avoid freezing and shaking.
⚠️Disclaimer:
At ePharma, we’re committed to providing accurate and accessible health information. However, all content is intended for informational purposes only and should not replace medical advice from a qualified physician. Please consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance. We aim to support, not substitute, the doctor-patient relationship.