✔ 100% Authentic Product
👁️ Currently Viewing 1176
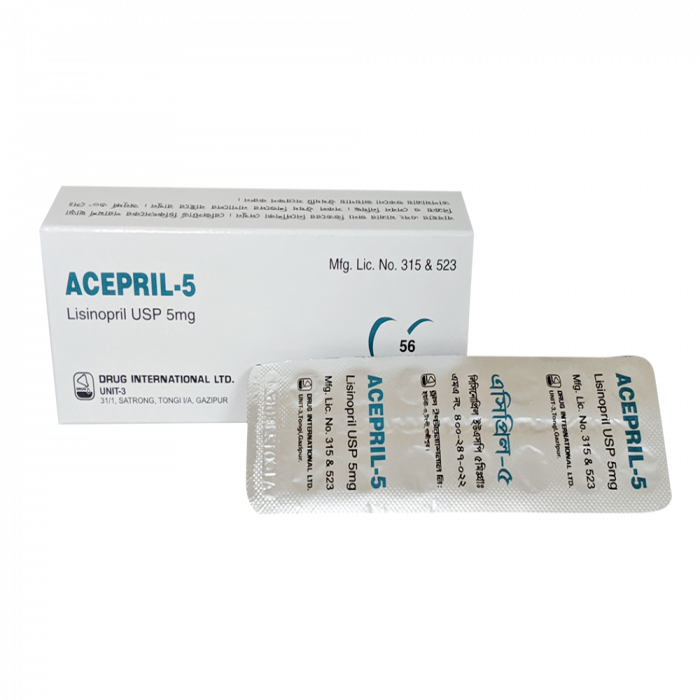
Type: Tab. Manufacturer/Distributor: Drug Inter. Generic Name: Lisinopril 5mg & 10mg/tablet
Discount
Price: ৳ 53
MRP:
৳
56.7
6%
Off

100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed

Safe & Secure Payments, Always

Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery

Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed
Safe & Secure Payments, Always
Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery
Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
✅ Description:
Indications
Hypertension: Lisinopril is used to treat hypertension in adults and children aged 6 and up. It lowers blood pressure. Lowering blood pressure reduces the risk of fatal and nonfatal cardiovascular events, such as strokes and myocardial infarctions. Antihypertensive medicines from a wide range of pharmacologic classes have shown these advantages in controlled trials.
High blood pressure control should be part of a complete cardiovascular risk management strategy that includes, where needed, cholesterol control, diabetes management, antithrombotic treatment, smoking cessation, exercise, and sodium restriction. To meet blood pressure targets, many individuals will require more than one medicine. See published guidelines, such as those of the National High Blood Pressure Education Program's Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure, for detailed advice on goals and management (JNC).
In randomized controlled trials, a variety of antihypertensive drugs from various pharmacologic classes and with various mechanisms of action have been shown to reduce cardiovascular morbidity and mortality, and it can be concluded that blood pressure reduction, not some other pharmacologic property of the drugs, is largely responsible for those benefits. The reduction in the risk of stroke has been the most significant and consistent cardiovascular outcome benefit, but reductions in myocardial infarction and cardiovascular mortality have also been shown on a regular basis.
Lisinopril is used to treat heart failure symptoms in patients who aren't responding well to diuretics or digitalis.
Acute Myocardial Infarction: Lisinopril is used to reduce mortality in hemodynamically stable patients who have had an acute myocardial infarction within the first 24 hours. Standard suggested treatments such as thrombolytics, aspirin, and beta-blockers should be given to patients as needed.
Pharmacology
Lisinopril inhibits ACE from converting angiotensin I to angiotensin II (a potent vasoconstrictor), resulting in higher plasma renin activity and lower aldosterone secretion (a hormone that causes water and sodium retention). This causes vasodilation and lowers blood pressure.
Dosage & Administration
Oral (Adult)-
Hypertension: Initially, 10 mg/day, 1st dose given preferably at bedtime to avoid precipitous fall in BP. Patient with renovascular HTN, volume depletion, severe HTN: Initially, 2.5-5 mg once daily. Patient on diuretic: Initially, 5 mg once daily. Maintenance: 20 mg once daily, up to 80 mg/day may be given if needed.
Diabetic nephropathy: Hypertensive type 2 diabetics with microalbuminuria: 10 mg once daily, may increase to 20 mg once daily to achieve a sitting diastolic BP
Heart failure: As adjunct: Initially, 2.5 or 5 mg/day, increased by increments of ≤10 mg at intervals of at least 2 wk to max maintenance dose of 40 mg/day.
Post-myocardial infarction: Initially, 5 mg once daily for 2 days started within 24 hr of the onset of symptoms. Increase to 10 mg once daily. Patients with low systolic BP: Initially, 2.5 mg once daily.
Oral (Child)-
Hypertension: ≥6 yr Initially, 0.07 mg/kg, up to 5 mg once daily.
Interaction
Diuretics may enhance the hypotensive effect. NSAIDs, it may increase the risk of renal function deterioration and reduce the antihypertensive effect. Lithium toxicity and serum levels may be affected. Hyperkalemia is a risk with K-sparing diuretics and K supplements. Gold Na thiomalate nitrite reactions may be boosted.
Contraindications
Previous ACE inhibitor treatment-related angioedema, hereditary or idiopathic angioedema. In patients with diabetes or renal impairment, aliskiren should be used together. Pregnancy. Children with a GFR of less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m2
Side Effects
Headache, fatigue, chest and abdominal pain, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, upper respiratory tract infection, asthenia, rash, orthostatic effects, hypotension, renal dysfunction, hyperkalemia, intestinal angioedema; increased BUN and serum creatinine levels.
Pregnancy & Lactation
Category D: Although there is evidence of human fetal risk, the benefits of use in pregnant women may outweigh the risk (e.g., if the drug is needed in a life-threatening situation or for a serious disease for which safer drugs cannot be used or are ineffective).
Precautions & Warnings
Bilateral renal artery stenosis or unilateral renal artery stenosis in a single kidney. Patients with collagen vascular disease and acute MI are at risk of worsening hemodynamics, angioedema not related to ACE inhibitor therapy, aortic stenosis, and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Angioedema risk is higher in black patients. Renal insufficiency. Lactation. 6 yr. old child
Storage Conditions
Store at a temperature of less than 25° C.
⚠️Disclaimer:
At ePharma, we’re committed to providing accurate and accessible health information. However, all content is intended for informational purposes only and should not replace medical advice from a qualified physician. Please consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance. We aim to support, not substitute, the doctor-patient relationship.