✔ 100% Authentic Product
👁️ Currently Viewing 1333
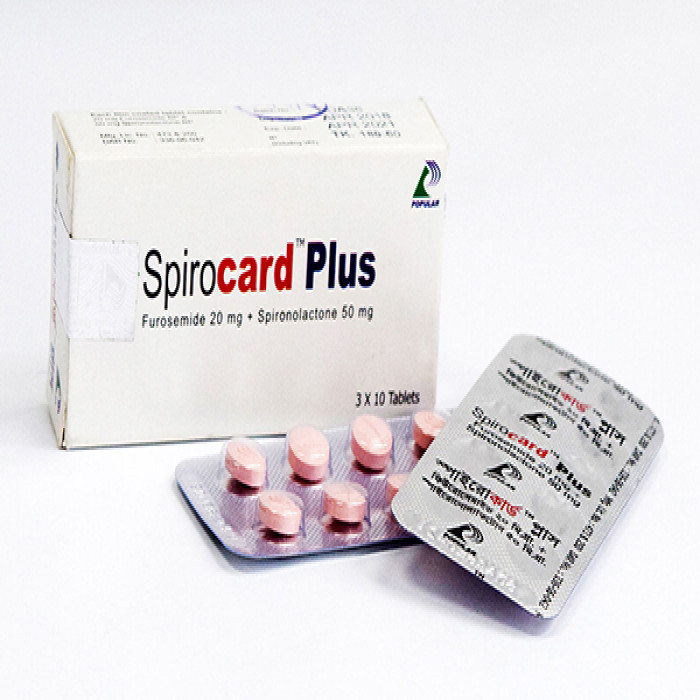
Generic Name: Furosemide 20mg + Spironolactone 50mg
Company name: Popular Pharmaceuticals Ltd.
Discount
Price: ৳ 75
MRP:
৳
80
6%
Off

100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed

Safe & Secure Payments, Always

Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery

Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed
Safe & Secure Payments, Always
Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery
Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59
Regular Delivery - 12-24 Hours, Dhaka City* Charge Tk.39-59 Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110
Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, Other Cities* Charge Tk.99-110 ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকা
শহরে ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
ফ্রি ডেলিভারিঃ - ২৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে, ঢাকার
বাহিরে
✅ Description:
Indications
The combination of frusemide and spironolactone is suggested in-
- Essential hypertension
- Congestive heart failure (CHF) is a type of congestive heart failure
- Cirrhosis of the liver with fluid buildup in the abdominal cavity (ascites)
- Excess fluid retention causes swelling (edema)
- Hyperaldosteronism
- Secondary hyperaldosteronism is related to resistant edema.
Pharmacology
Spironolactone (potassium-saving diuretic) and Furosemide (circle diuretic) have diverse but complementary instruments and locales of activity. Subsequently, when given together they create added substance or synergistic diuretic. The Furosemide component represses the Na+/K+/2Cl- co-transporter within the climbing Circle of Henle and squares the reabsorption of sodium, potassium, and chloride particles; in this manner expanding the amount of sodium and the volume of water excreted within the pee. This characteristically actuates potassium misfortune. The spironolactone component restrains the reabsorption of sodium in trade for potassium at the distal tubule by irritating the activity of aldosterone so that sodium excretion is enormously favored and the abundance misfortune of potassium, actuated by the Furosemide, is reduced
Dosage & Administration
Furosemide 20 and spironolactone 50 mg: 1 to 4 tablets daily (20 to 80 mg of Furosemide and 50 to 200 mg of spironolactone) according to the patient’s response.
Furosemide 40 and spironolactone 50 mg: For previously stabilized patients requiring a higher dosage of spironolactone and Furosemide, This tablet can be used at a dose of one to two tablets daily (Furosemide 40 to 80 mg and spironolactone 50 to 100 mg).
Use in children: Spironolactone and Furosemide are not suitable for use in children. Spironolactone and Furosemide may both be excreted more slowly in the elderly.
Interaction
When taken in conjunction with Expert inhibitors or potassium salts there's an expanded risk of hyperkalemia. Spironolactone increments the levels of cardiac glycosides such as digoxin within the blood and this may result in digitalis harmfulness. Corticosteroids may cause hypokalemia in the event that they are utilized with Spironolactone. The blood weight bringing down and diuretic impacts of Furosemide may be diminished or canceled when utilized along with indomethacin and conceivably other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Furosemide may increment the ototoxicity of aminoglycoside anti-microbials. Concurrent organization of sucralfate and Furosemide may decrease the natriuretic and anti-hypertensive impact of Furosemide.
Contraindications
Anuria, acute renal insufficiency, quickly deteriorating or severe impairment of renal function (creatinine clearance 30 ml/min), hyperkalemia, Addison's disease, and hypersensitivity to Spironolactone, Furosemide, or sulphonamides are all contraindications.
Side Effects
Spironolactone may deliver rise to migraine and laziness and gastrointestinal trouble, counting spasms and runs. Ataxia, mental perplexity, and skin rashes have been detailed as a side impacts. Gynaecomastia isn't unprecedented and in uncommon cases, breast extension may endure. Other endocrine disarranges counting hirsutism, an extension of the voice, menstrual inconsistencies, and weakness. Temporal increment in blood-urea-nitrogen concentrations may happen and mellow acidosis has been detailed. Spironolactone may cause hyponatremia and hyperkalemia. Intemperate diuresis may result in a lack of hydration and a decrease in blood volume with circulatory collapse with the plausibility of vascular thrombosis and embolism, especially in elderly patients. Genuine consumption of potassium and magnesium may lead to cardiac arrhythmias.
Pregnancy & Lactation
Spironolactone and its metabolites may pass the placental barrier during pregnancy. When using spironolactone in pregnant women, the expected benefit must be evaluated against the potential risks to the mother and fetus. Furosemide may induce prenatal malformations, according to animal teratology studies. As a result, furosemide should only be used in women of childbearing age if proper contraception is employed or if the possible benefits outweigh the hazards to the fetus.
Lactation: Spironolactone metabolites have been found in breast milk. If the usage of Spironolactone is deemed necessary, an alternative infant feeding strategy should be implemented. Furosemide is excreted in breast milk, therefore if you need to take it, you should stop breastfeeding.
Precautions & Warnings
In patients who are at risk of electrolyte shortage, caution is advised. In diabetes, enlarged prostate, hypotension, and hypovolemia, this product should be taken with caution.
Storage Conditions
Keep below 30°C temperature, away from light & moisture. Keep out of the reach of children.
⚠️Disclaimer:
At ePharma, we’re committed to providing accurate and accessible health information. However, all content is intended for informational purposes only and should not replace medical advice from a qualified physician. Please consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance. We aim to support, not substitute, the doctor-patient relationship.