✔ 100% Authentic Product
👁️ Currently Viewing 246
100% Genuine Products, Guaranteed
Safe & Secure Payments, Always
Fast, Secure & Efficient Delivery
Proper Packaging
 Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh
Cash on Delivery - All over Bangladesh Regular Delivery - 8-12 Hours, Dhaka City
Regular Delivery - 8-12 Hours, Dhaka City Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, All Over Bangladesh
Regular Delivery - 24-48 Hours, All Over Bangladesh ফ্রি ডেলিভারি! - ৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে ঢাকা
শহরে ।
ফ্রি ডেলিভারি! - ৯৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে ঢাকা
শহরে । ফ্রি ডেলিভারি! - ২৪৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে ঢাকার
বাহিরে ।
ফ্রি ডেলিভারি! - ২৪৯৯ টাকা+ অর্ডারে ঢাকার
বাহিরে ।
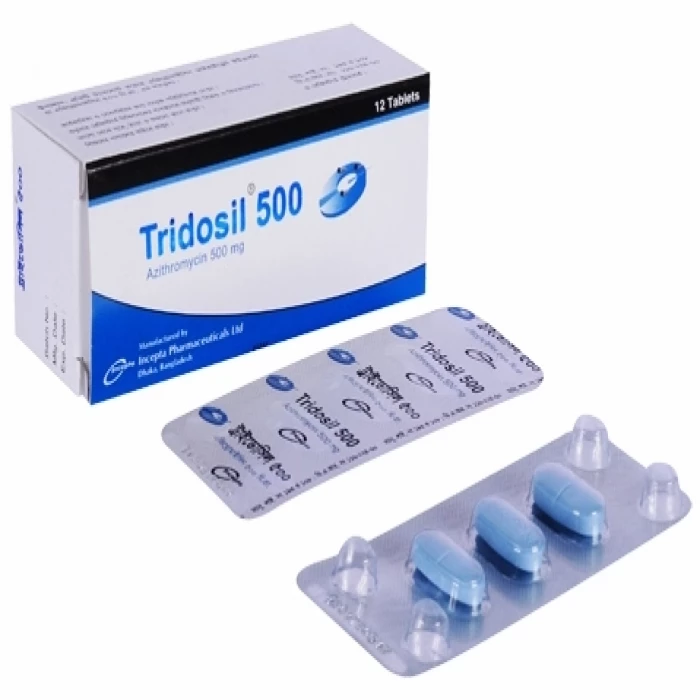
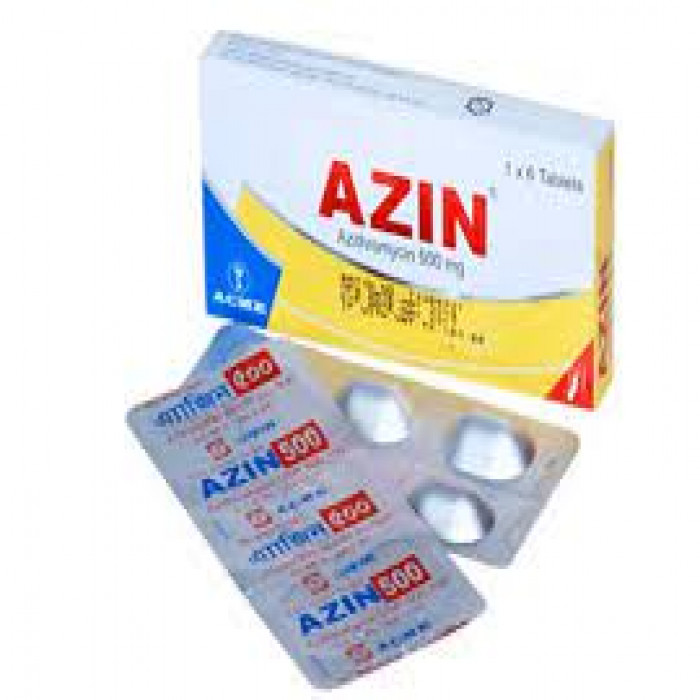
✅ Description:
Indications
Azin 500 is an antibiotic that is used in adults and children to treat bacterial infections of the respiratory tract, ear, nose, throat, lungs, skin, and eyes. It is also useful in the treatment of typhoid fever and some sexually transmitted diseases such as gonorrhea. Azin 500 is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that is effective against many gram-positive bacteria, some gram-negative bacteria, and other microorganisms. This medication is taken orally, preferably one hour before or two hours after eating. It should be taken on a regular basis at evenly spaced time intervals, as directed by your doctor.
Pharmacology
Azithromycin is acid-stable, so it can be taken orally without fear of being destroyed by stomach acids. It is quickly absorbed; its retention is more noticeable on a purge stomach. For verbal measurement shapes, the time to crest concentration in adults ranges from 2.1 to 3.2 hours. Because of its high concentration in phagocytes, azithromycin is efficiently transported to the site of the disease. Azithromycin in high concentrations is released during dynamic phagocytosis. Azithromycin concentrations in tissues can be more than 50 times higher than in plasma. This is frequently caused by particle catching and high lipid dissolvability.
Dosage & Administration
Oral
Adult:
- 500 mg orally once daily for three days, or 500 mg once on day one, then 250 mg once on days two through five for four days.
- Adults with sexually transmitted diseases caused by Chlamydia trachomatis should receive 1 gm as a single dose, or 500 mg once on day 1, followed by 250 mg once daily for the next two days.
Children:
- 10 mg/kg body weight once daily for three days for children over the age of six months;
- 200 mg (1 teaspoonful) once daily for three days if body weight is 15-25 kg;
- 300 mg (112 teaspoonfuls) once daily for three days if body weight is 26-35 kg;
- 400 mg (2 teaspoonfuls) once daily for three days if body weight is 36-45 kg.
- Typhoid fever is treated with 500 mg (212 teaspoonfuls) once daily for 7-10 days.
Interaction
The proximity of nourishment and stomach-settling agent decreases azithromycin absorption. Azithromycin should be avoided in patients who are taking ergot alkaloids because of the possibility of ergotism caused by Azithromycin's interaction with the cytochrome P-450 framework. Because macrolides increase the plasma concentrations of digoxin and cyclosporin, caution should be exercised when co-administration. There is no evidence of a therapeutic relationship between Azithromycin and Warfarin, Theophylline, Carbamazepine, Methylprednisolone, or Cimetidine.
Contraindications
Patients who are hypersensitive to azithromycin or any other macrolide antibiotic should avoid taking it. Ergot derivatives and azithromycin should not be taken together. Patients with hepatic disorders should avoid azithromycin.
Side Effects
Azithromycin is a well-tolerated antibiotic with few adverse effects. Nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort (pain/cramps), flatulence, diarrhea, headache, dizziness, and skin rashes are among the side effects, which are reversible as the medication is stopped.
Pregnancy & Lactation
The pregnancy Category of Azithromycin is B. Creature generation thinks about has illustrated that Azithromycin has no proof of hurt to the embryo. There are no satisfactory and well-controlled thinks about in pregnant ladies. Since creature generation ponders are not continuously prescient of human reaction, Azithromycin ought to be utilized amid pregnancy as it were on the off chance that satisfactory choices are not accessible. It isn't known whether Azithromycin is discharged in breast drain. So, caution ought to be worked out when Azithromycin is managed to nursing ladies.
Precautions & Warnings
Observation for signs of superinfection with non-susceptible organisms, especially fungus, is suggested with any antibiotic. In patients with renal impairment, there is no need to alter the dose.
Storage Conditions
Keep the temperature below 30°C and away from light and moisture. Keep out of children's reach.
Disclaimer:
ePharma sole intention is to ensure that its consumers get proper
information as musch as possible. Although we do not guarantee the
accuracy and the completeness of the information that provided and
here information is for informational purposes only.
The information contained herein should NOT be used as a substitute
for the advice of a qualified physician. This may not cover
everything about particular health conditions,
lab tests, medicines, all possible side effects, drug interactions,
warnings, alerts, etc. Please consult your healthcare professional
and discuss all your queries related to any disease or medicine. We
intend to support, not replace, the doctor-patient relationship.