✔ 100% Authentic Product
👁️ Currently Viewing 1067
✅ Description:
Indications
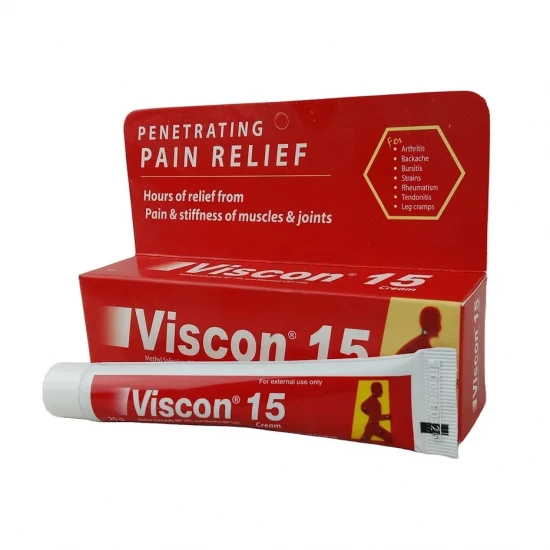
For the treatment of mild to moderate pain and fever. Paraserts/Paracetamol Suppositories may be especially useful in patients unable to take oral forms of paracetamol, e.g. post-operatively or with nausea and vomiting.
Posology and method of administration
Method of administration: rectal
Children:
1 year – 5 years: 1 -2 suppositories every 4 to 6 hours.
Dosages should be based on the child's age and weight i.e.:
1 year (10 kg) – 125 mg (1 suppository)
5 years (20 kg) – 250 mg (2 suppositories)
These doses may be repeated up to a maximum of 4 times in 24 hours. The dose should not be repeated more frequently than every 4 hours. The recommended dose should not be exceeded. Higher doses do not produce any increase in analgesic effect. The product should not be used for more than 3 days, except on the advice of a doctor. Only whole suppositories should be administered – do not break the suppository before administration
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the active substance, to any of the excipients listed in section 6.1, soy or peanuts.
Special warnings and precautions for use
Paraserts/Paracetamol Suppositories should not be combined with other analgesic medications that contain paracetamol. Paracetamol should be given with care to patients with impaired kidney or liver function.
In general, the habitual use of painkillers, especially with combinations of more than one pain killing active ingredient, can lead to permanent kidney damage with the risk of liver failure (analgesic nephropathy).
Label and leaflet will state the following warnings:
Label:
“Immediate medical advice should be sought in the event of an overdose, even if the child seems well”.
“Do not give with any other Paracetamol-containing products.”
Leaflet:
“Immediate medical advice should be sought in the event of an overdose, even if the child seems well, because of the risk of delayed, serious liver damage.”
Caution is advised if paracetamol is administered concomitantly with flucloxacillin due to increased risk of high anion gap metabolic acidosis (HAGMA), particularly in patients with severe renal impairment, sepsis, malnutrition and other sources of glutathione deficiency (e.g. chronic alcoholism), as well as those using maximum daily doses of paracetamol. Close monitoring, including measurement of urinary 5-oxoproline, is recommended.
Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
The absorption of paracetamol is speeded by metaclopramide or domperidone, and absorption is reduced by colestyramine.
The anticoagulant effect of warfarin and other coumarins may be increased by long term regular daily use of paracetamol, with increased risk of bleeding. Occasional doses of paracetamol do not have a significant effect on these anticoagulants.
Enzyme-inducing medicines, such as some antiepileptic drugs (phenytoin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine) have been shown in pharmacokinetic studies to reduce the plasma AUC of paracetamol to approx. 60 %. Other substances with enzyme- inducing properties, e.g. rifampicin are also suspected of causing lowered concentrations of paracetamol. In addition, the risk of liver damage during treatment with maximum recommended doses of paracetamol will be higher in patients being treated with enzyme-inducing agents.
Caution should be taken when paracetamol is used concomitantly with flucloxacillin as concurrent intake has been associated with high anion gap metabolic acidosis, especially in patients with risk factors
Epidemiological studies in human pregnancy have shown no ill effects due to paracetamol used in the recommended dosage, but patients should follow the advice of their doctor regarding its use.
Paracetamol is excreted in breast milk but not in clinically significant amounts. Available published data do not contraindicate breast feeding.
⚠️Disclaimer:
At ePharma, we’re committed to providing accurate and accessible health information. However, all content is intended for informational purposes only and should not replace medical advice from a qualified physician. Please consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance. We aim to support, not substitute, the doctor-patient relationship.